Finding the minimum sub-string
Problem
Given the input string str1 and the seed string str 2, write the program to find the minimum sub-string of str1 that is inclusive of str 2.
Example)
Case 1) str1 = "abbcbcba" and str2 = "abc", answer = "cba"
Case 2) str1 = "caaababc" and str2 = "abc", answer = "abc"
Similiarity
This question is very similar to the "finding the minimum sub-sequence given three strings" except for the additional string that should not be included.Brute-force recursive approach
Inefficient but simplest way is to search from the beginning of the input string, str1 and try the all the possible permutation which contains str2. Algorithm will be like as below:
1. create the map containing the letters in str2 along with its occurrence count
2. for i to str1.len then ==> $O(N)$
2-1. try all substrings starting from str1[i] and find the sub string contains str2. ==>$O(N)$
2-2. check if found string is the smaller then the previously found string
3. return the smallest substring.
Running time of this approach will be $O(N^2)$
Pervious algorithm does get the results but it is not efficient. It examines the same substring multiple times.
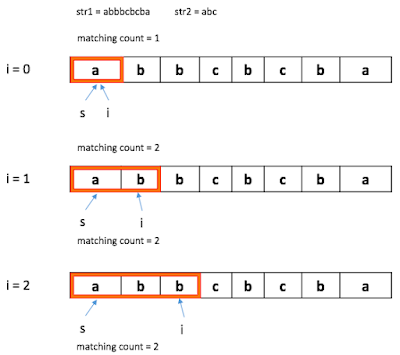
Better way is what I call, moving window approach. See the following illustration.
In this algorithm, the window start with the one character and increase each iteration. In doing so, the count of matching letters, matching count is also counted. If the matching count becomes 3 as in the last iteration in Figure 3. We take the sub string from s to i and store it.
After that, the algorithm reduces the window from the left as long as the matching count is 3. If matching count become 2 as in Figure 2, the window start growing to the right again following the same rules in Figure 1 until the next substring is found.
Each time new substring is found, only shortest sub string is stored or ignored otherwise.
In this algorithm, we reduce the previous letters after finding the candidate substring, which removes the chances of examining the same substrings as in the brute force approach.
Running time of this approach will be $O(N)$.
Here is complete code of DFS approach
1. create the map containing the letters in str2 along with its occurrence count
2. for i to str1.len then ==> $O(N)$
2-1. try all substrings starting from str1[i] and find the sub string contains str2. ==>$O(N)$
2-2. check if found string is the smaller then the previously found string
3. return the smallest substring.
Running time of this approach will be $O(N^2)$
Better approach with moving window
Pervious algorithm does get the results but it is not efficient. It examines the same substring multiple times.
Better way is what I call, moving window approach. See the following illustration.
 |
| Figure 1. Algorithm illustration. |
After that, the algorithm reduces the window from the left as long as the matching count is 3. If matching count become 2 as in Figure 2, the window start growing to the right again following the same rules in Figure 1 until the next substring is found.
Each time new substring is found, only shortest sub string is stored or ignored otherwise.
In this algorithm, we reduce the previous letters after finding the candidate substring, which removes the chances of examining the same substrings as in the brute force approach.
Running time of this approach will be $O(N)$.
Here is complete code of DFS approach
Here is the complete code of moving window approach
Python version of moving window scanning
Python version of brute-force search
Practice statistics
Python version of moving window scanning
Python version of brute-force search
Practice statistics
33:00 to write up the DFS approach
20:00 to write up the moving window approach

Comments
Post a Comment